ADAS Overview
You may be familiar with this term. We have heard of "ADAS" from many brands of high-end models, driving recorders or smart cloud mirror configurations. ADAS advanced driver assistance calibration equipment is famous for its powerful predictive and risk avoidance capabilities. What are the specific applications of ADAS? What is the essential difference between ADAS and autopilot?
ADAS is the abbreviation of Advanced Driver Assistance System, which is translated into Chinese as Advanced Driver Assistance System. In short, ADAS refers to making active judgments and preventive measures before the driver's subjective reaction to emergencies to achieve the functions of prevention and assistance. We can call it a simplified version of autonomous driving - ADAS Advanced Assisted Driving System.
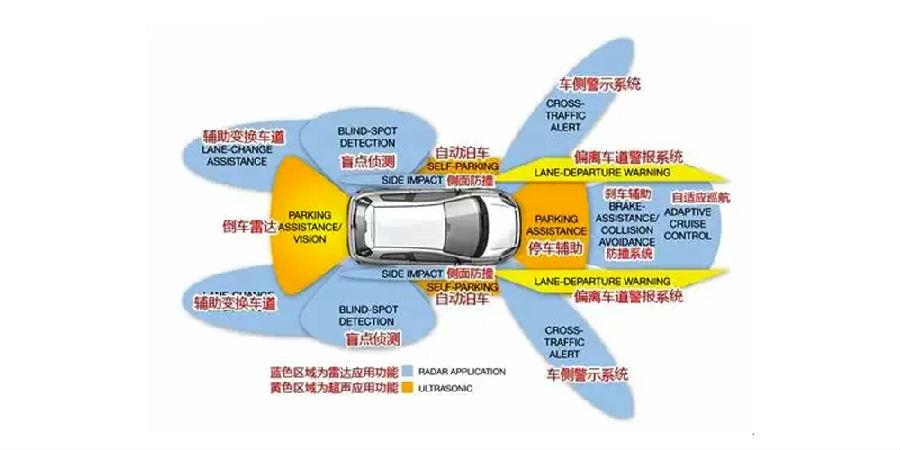
Here we need to make a clear concept. ADAS is not the very popular autonomous driving. It can be said that the two research focuses are completely different. ADAS is assisted driving, and its core is environmental perception, while autonomous driving is artificial intelligence, which has very different systems. However, ADAS can also be regarded as a prerequisite for self-driving cars. To determine whether a system is an autonomous driving system or an autonomous driving system, the key is whether the system has a decision-making part.
ADAS function classification
ADAS advanced driver assistance calibration equipment configuration includes the following 17: navigation, TMC real-time traffic system, electronic police system ISA, car network, adaptive cruise ACC, lane migration Changchun, lane keeping system, alarm system to avoid collision or collision system, night vision system, adaptive lighting control, pedestrian collision warning system, automatic parking, traffic sign recognition, blind spot detection, driver fatigue detection, downhill control system, electric vehicle alarm system. Common ADAS segmentation functions include lane departure warning system (LDW), front collision warning system (combined), blind spot monitoring system (BSD), lane change assist system (LCA), adaptive cruise system (ACC), automatic emergency braking (AEB), automatic parking system (APS), intelligent speed assist system (ISA), lane keeping system (road), driver status monitoring system (crane group), etc.
It is understood that the current assembly rate of BSD is the highest, at 7.53%, followed by LDW and FCW, at 7.4% and 6.83% respectively. For other segmentation functions, the current assembly rate of AEB is about 6.48%, the assembly rate of APS is 4.58%, and the assembly rate of ACC is 4.44%.
The relationship between autopilot and ADAS
Autonomous driving is the ultimate goal of advanced driver assistance, and ADAS belongs to L2 level (partial autonomy) of autonomous driving. On the road to L5 autonomous driving, the maturity and perfection of the ADAS system is the basic guarantee. As far as the current technology is concerned, the ADAS system needs to break through the accuracy of external information collection and data processing capabilities. The former is the combination of high-precision photography and laser radar, and the latter is MCU, GPU or GPU plus FPGA and other professional vehicle processing chips. Of course, with the development of high-precision maps.
Components required for ADAS advanced driver assistance calibration equipment technology
Adaptive cruise control: radar, radar and camera
Forward Collision Warning System: Radar, Camera, Infrared Sensor
Pedestrian detection system: radar, camera
Traffic signal and sign recognition: cameras, map data
Lane departure warning system: camera, infrared sensor
Blind spot detection system: ultrasonic sensor, camera, infrared sensor
Night vision system: near infrared sensor and far infrared sensor
Attention detection system: infrared camera
Related News
- How does the dynamic four wheel aligner avoid communication interference?
- Introduction to vehicle electrical inspection
- How to choose a good pass four wheel aligner
- What is the assembly line
- The important role of the through four wheel aligner
- The four main points of 3D laser four wheel aligner maintenance
- Working principle of electric chassis dynamometer
- Vehicle off-line comprehensive diagnostic equipment
- How to choose a good dynamic four wheel aligner
- Precautions for selecting a non-contact four-wheel aligner
- Measurement advantages of 3D laser 4 wheel alignment
- A Brief Discussion on Electric Chassis Dynamometer
- How to ensure the normal operation of the through-type 4-wheel alignment instrument
- Usage and maintenance of dynamic 4-wheel alignment instrument
- What are the misconceptions car owners have about non-contact 4-wheel alignment
- What is the importance of dynamic 4 wheel alignment nowadays?
- Let's understand the dynamic 4 wheel alignment market
- Comparison of the characteristics and cost analysis of 3D dynamic positioning platform and static 3D positioning instrument
- Comparison between dynamic 4 wheel aligners and static aligners
- What is the difference between a static 4-wheel alignment instrument in a repair shop and a dynamic surface measurement 4-wheel alignment instrument in a car factory?
